Alcohols: Synthesis and Chemical Reactions
Alcohols are a class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group attached to a carbon atom. This functional group imparts distinctive chemical and physical properties to alcohols, making them a versatile group of compounds with a wide range of applications.
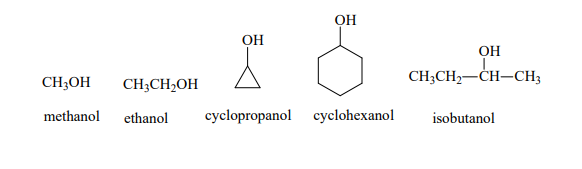
Alcohols can be classified based on the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon bearing the hydroxyl group. The simplest alcohol is methanol , followed by ethanol , which is the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages. As the carbon chain lengthens, we encounter a variety of alcohols, each with unique properties and uses.
The general formula for simple acyclic alcohol is , where .
The saturated carbon chain is often designated by the symbol , so that can represent alcohol in the homologous series.